What Is Leukemia?
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, the spongy center of bones where our blood cells are formed. The disease develops when blood cells produced in the bone marrow grow out of control.
An estimated 52,380 new cases of leukemia are expected to be diagnosed in the United States in 2014.
What Is AML?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the bone marrow and the blood that progresses quickly without treatment. It affects mostly cells that aren’t fully developed. These cells can’t carry out their normal functions. That’s one reason why it’s important to get care and treatment as soon as possible.
With treatment, people who have AML continue to see improved results. However, AML can be a difficult disease to treat, and researchers are studying new approaches to AML therapy in clinical trials.
AML is also called:
Source: Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Reviewed by Judith Karp, MD.
To learn more about Leukemia and AML, please visit the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society website.
American Cancer Society Report
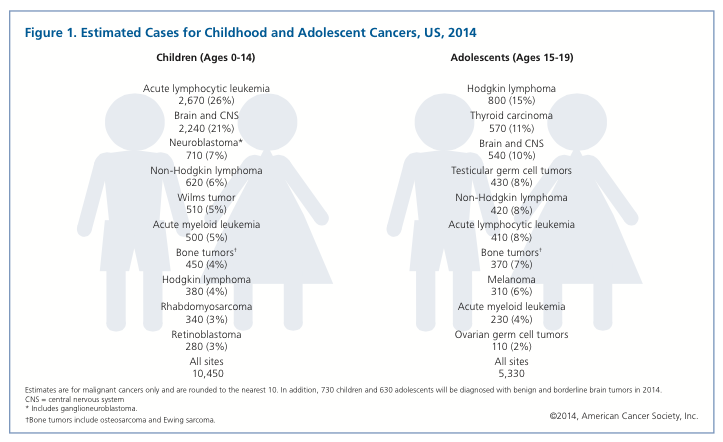
The news of a cancer diagnosis is never welcome, but may be even more unexpected and difficult when the disease is diag- nosed in a child or adolescent. Although cancer is much less common among children compared to older adults, approxi- mately 1 in 285 children in the US will be diagnosed with the disease before the age of 20. While advances in treatment have increased the survival rate for many childhood cancers, the dis- ease is still the second leading cause of death (following accidents) in children ages 5-14.1
Click on this chart to see the projected number of adolescents who will be diagnosed with cancer (more specifically, AML) in 2014.
To read the American Cancer Society’s Report on Children’s Cancer, click the button below.